Introducing the Time in Range Coalition
diaTribe created the Time in Range Coalition to increase awareness and adoption of time in range – a metric that empowers people with diabetes through information. Read below to learn more about the Coalition and why we are advocating for time in range.
At The diaTribe Foundation, we believe that Time in Range (TIR) should be used in diabetes care to give people with diabetes the information they need to manage the disease. That is why diaTribe created the Time in Range Coalition – a multi stakeholder group of companies, foundations, nonprofits, clinicians, and researchers committed to advancing the use of TIR in diabetes care.
TIR is the percentage of time that a person spends in a target blood glucose range. The target range can vary by person but guidelines recommend that people with diabetes stay in a range of 70-180 mg/dl. Learn more here.
What are the Goals of the Time in Range Coalition?
The main objective of the Time in Range Coalition is to ensure that TIR becomes the primary glucose metric for daily management, complemented by A1C, in diabetes care globally. To accomplish this, the Coalition is focused on the following priority areas:
- People with Diabetes - Increase the adoption and use of TIR for daily disease management among people with diabetes.
- Healthcare Providers - Increase the adoption and use of TIR for daily disease management among healthcare providers.
- Regulatory & Policy - Advocate for TIR to be used in diabetes research and regulatory decision-making.
Since forming the Coalition in 2019, we have had several notable achievements that have brought us closer to our Coalition objectives. We have published over 80 articles about TIR on diaTribe Learn and diaTribe Change that have reached well over 600,000 people with diabetes, their caretakers, and healthcare providers. To inform how we can best raise awareness for TIR across people with diabetes and Healthcare providers, the Coalition has initiated two comprehensive market research projects to understand current perceptions and awareness on the topic. The Coalition has also met with the FDA, the agency that ensures the safety, efficacy, and quality of drugs and devices, to discuss the clinical evidence supporting the use of TIR in diabetes management. These achievements, among others, are increasing the adoption of TIR among people with diabetes, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies.
Why Use Time in Range?
TIR goes beyond A1C in analyzing blood glucose levels because it provides a more complete picture of glycemic control, including the percent of time glucose levels are in target range as well as the percent of time levels are high and low. This information is important to understand when managing diabetes. While A1C is commonly used as an average measure of blood glucose over a span of 2-3 months, it does not capture glucose variability which can affect the health of people with diabetes.
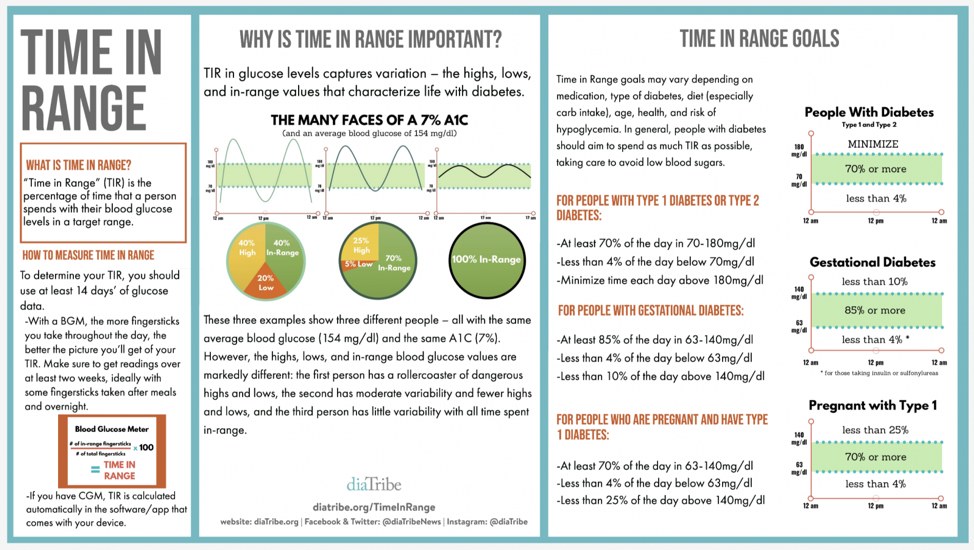
The diagram below is an example of three different people with diabetes, all who have an A1C of 7%. As you can see, the example on the left has dangerous highs and lows while the person on the right is 100% in-range. High and low blood sugars can impact energy levels, moods, and can cause serious health complications in the short and long term. A1C alone does not capture the overall picture of glycemic control but with the addition of TIR, people with diabetes can have the information they need to take control of their diabetes.
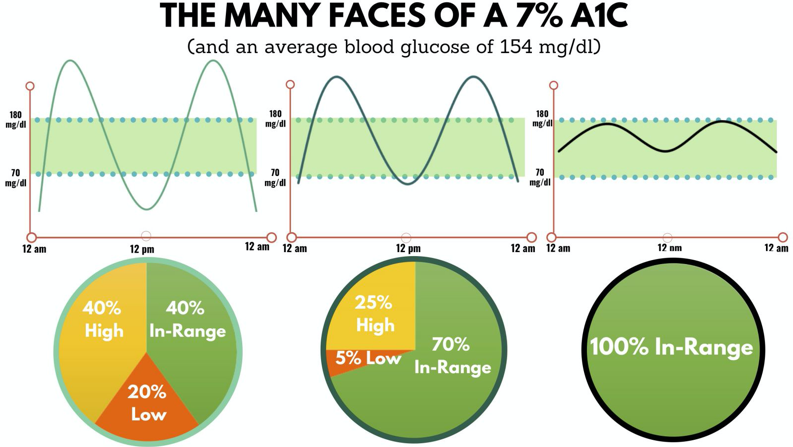
TIR is typically measured using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). While a person with diabetes only gets an A1C test every 2-3 months, they can see TIR on their CGM on a daily basis. TIR gives people with diabetes immediate feedback they can use to understand what causes highs and lows and how to address them. Empowering people to increase their time in range while reducing highs and lows can improve their health and quality of life.
Look here for more information on TIR.
With the support of our Coalition members, we are working to increase the adoption of TIR to make diabetes care better and easier for people with diabetes. See below for a list of our Coalition members.
Executive Steering Committee Members

Steering Committee Members

Advisory Board Members

Members